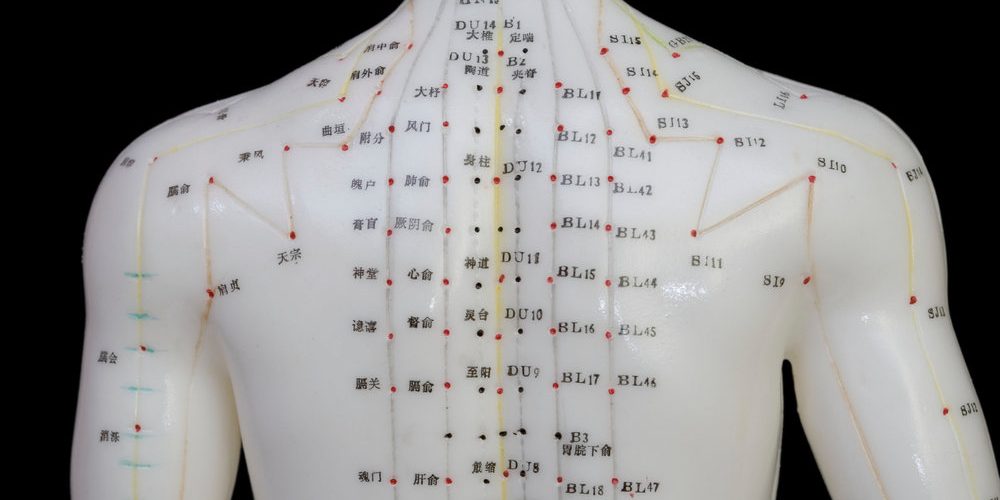
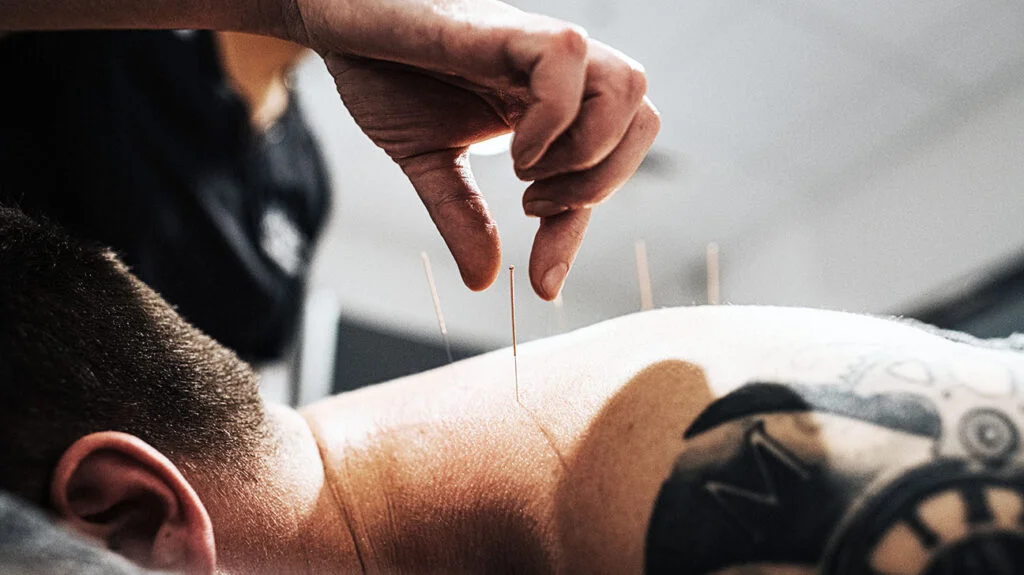
Acupuncture, an ancient healing practice originating from traditional Chinese medicine, involves the insertion of fine needles into specific points on the skin to address various health issues. This technique, which has been in existence for over 2,500 years, has garnered global recognition since the 1970s.
The Reach of Acupuncture:
The World Health Organization reports that acupuncture is utilized in 103 out of 129 countries with available data. In the United States, the National Health Interview Survey indicates a significant surge in acupuncture usage, with a 50 percent increase between 2002 and 2012. In 2012 alone, 6.4 percent of U.S. adults reported having tried acupuncture, with 1.7 percent receiving treatment within the previous 12 months.
Applications of Acupuncture:
Primary data from national surveys in the U.S. reveal that acupuncture is predominantly sought for pain management, particularly for issues like back, joint, or neck pain.
The Scientific Underpinnings:
While the precise mechanisms of acupuncture are not fully elucidated, studies suggest its impact on the nervous system, body tissues, and nonspecific (placebo) effects. Research involving both animals and humans, including neuroimaging studies, indicates that acupuncture can influence nervous system functioning. Additionally, it appears to exert direct effects on the tissues at needle insertion sites, particularly within connective tissue. Nonspecific effects, stemming from patient beliefs, practitioner-patient relationships, or other incidental factors, also contribute to its efficacy. Notably, studies comparing acupuncture with sham procedures underscore the role of nonspecific effects in pain relief, emphasizing the complex interplay of factors in its effectiveness.
Efficacy in Pain Management:
Accumulating evidence suggests the efficacy of acupuncture in alleviating various pain conditions, including back and neck pain, osteoarthritis-related knee pain, postoperative discomfort, and joint pain induced by aromatase inhibitors in breast cancer treatment. An analysis of multiple studies encompassing over 6,000 participants underscores the enduring benefits of acupuncture, persisting up to a year post-treatment cessation for most pain conditions.
Acupuncture stands as a multifaceted therapeutic approach with a rich history and growing scientific validation, offering promising avenues for pain relief and holistic wellness.